本文介绍了OTP的原理与实现。
技术规范
The service provider generates an 80-bit secret key for each user (whereas RFC 4226 §4 requires 128 bits and recommends 160 bits). This is provided as a 16, 26 or 32 character base32 string or as a QR code. The client creates an HMAC-SHA1 using this secret key. The message that is HMAC-ed can be:
the number of 30-second periods having elapsed since the Unix epoch (TOTP); or the counter that is incremented with each new code (HOTP). A portion of the HMAC is extracted and converted to a six-digit code.
伪代码实现
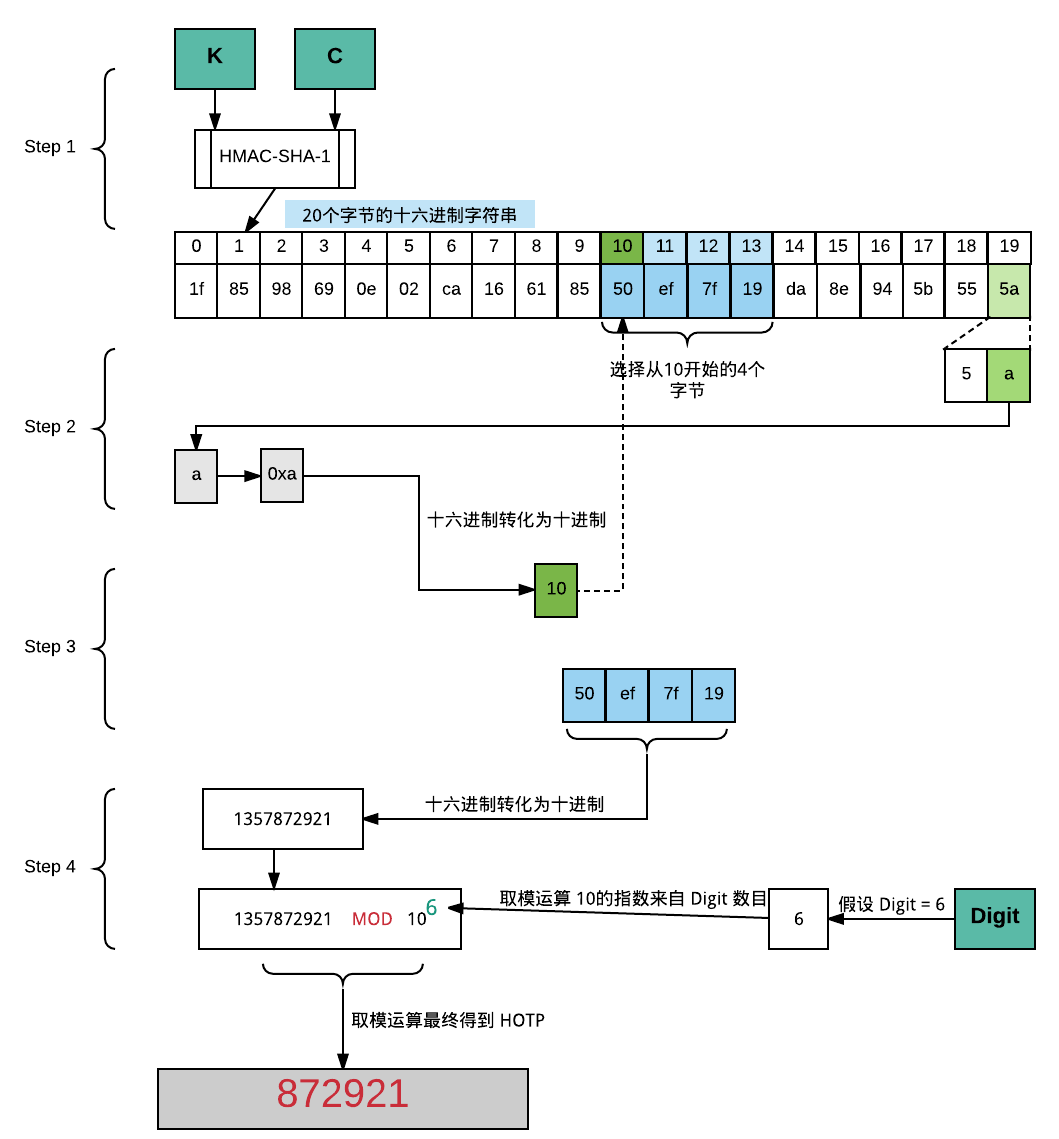
function GoogleAuthenticatorCode(string secret)
key := 5B5E7MMX344QRHYO
message := floor(current Unix time / 30)
hash := HMAC-SHA1(key, message)
offset := last nibble of hash
truncatedHash := hash[offset..offset+3] //4 bytes starting at the offset
Set the first bit of truncatedHash to zero //remove the most significant bit
code := truncatedHash mod 1000000
pad code with 0 from the left until length of code is 6
return code
Python实现
import pyotp
totp = pyotp.TOTP("JBSWY3DPEHPK3PXP")
print("Current OTP:", totp.now())
# OTP verified for current time
totp.verify('118427') # => False
uri = pyotp.totp.TOTP('JBSWY3DPEHPK3PXP').provisioning_uri("[email protected]", issuer_name="PyOTP")
print(uri)
生成二维码
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<canvas id="qr"></canvas>
<script src="qrious.min.js"></script>
<script>
(function() {
var qr = new QRious({
element: document.getElementById('qr'),
value: 'otpauth://totp/PyOTP:wanglifeng%40example.com?secret=JBSWY3DPEHPK3PXP&issuer=PyOTP',
size: 400
});
})();
</script>
</body>
</html>

